

The Association for Educational Communications and Technology (AECT) defines instructional design as “the theory and practice of design, development, utilization, management, and evaluation of processes and resources for learning” (Reiser, 2002, p. 1). The role of instructional design is often misunderstood. Perhaps this is because while the term “industrial design” is a fairly common one, the concept of instructional design is one that many people are unfamiliar with. So when they encounter the term “instructional design” for the first time, they may mistakenly assume that it is just another branch of the industrial design field that deals with various kinds of engineering. This confusion may lead to the idea that the role of instructional designers is similar to that of architects, draftspersons, computer programmers, or mechanical engineers. But in reality, instructional design does not involve any of the processes commonly associated with industrial design, such as engineering, construction, or product fabrication. Rather, instructional design is the science of creating instructional curriculum that is geared towards producing specific learning outcomes, based not only on pedagogical research, but also on current instructional practices. Although instructional design per se has nothing to do with computer programming or graphic design, these skills are extremely useful in producing effective curriculum, which is why usually individuals with such skills are included as part of the team designing courses. Having said that, it is worthwhile noting that while the implementation of certain technological resources can enhance and enrich learning outcomes, the end goal is effective instruction, not the production of technology-rich materials. In essence, then, the role of instructional design is to create instructional experiences that facilitate the acquisition of knowledge in a way that is not only efficient, but effective and appealing to learners. As a framework for developing learning modules, the focus of instructional design is on enhancing the learning acquisition process with the goal of engaging, encouraging, and motivating learners to gain deeper, more significant, and more meaningful levels of understanding and knowledge.
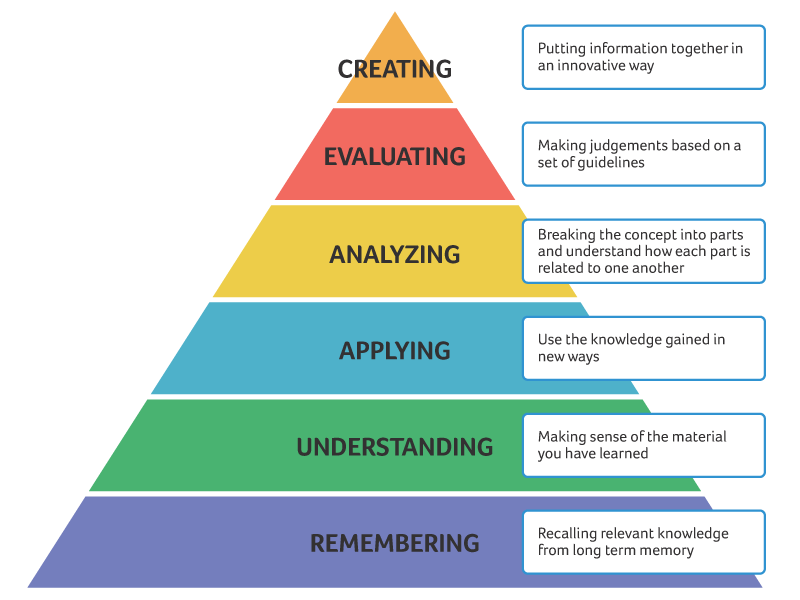
Historically, it is often thought that instructional design emerged in response to the need, during WW2, for the United States to rapidly train the thousands of new recruits enlisting in the armed forces. In fact, it was during this time period that a new term, “instructional technologist,” was first used. However, the actual conceptual roots of industrial design can be found in the work of early behavioral theorists Thorndike and Watson, and more recently, Pressey and Skinner. Perhaps the most accurate way of describing the history of instructional design is to say that it arose as a response, on the one hand, to the burgeoning empirical research in psychology and education, and on the other, to specific needs of the educative system as a whole. One of the most influential individuals in the field is certainly Benjamin Bloom, whose highly respected taxonomy was published in 1965. According to Bloom, learning objectives can be classified into three specific domains: affective; cognitive; and psychomotor. In 1965, Robert Gagne expanded upon this classificatory model. While his work retained the three primary classifications defined by Bloom, he also defined five learning outcomes (verbal information, intellectual skills, cognitive strategy, attitude, and motor skills), as well as nine instructional events that comprise the “conditions of learning.” Gagne’s work became, and still remains, the foundational basis of instructional design practices. However, over the past decade or so, the advent of online learning has allowed instructional designers new opportunities not only to learn about, but also to enrich, the instructional experiences available to learners. For instance, innovative technologies capable of sophisticated simulation of genuine, realistic learning experiences have provided designers with additional insight into how to enrich and improve education programs, including those delivered online.
References:
Reiser, R.A and Dempsey, J.V. (Eds.) (2002). Trends and Issues in Instructional Design and Technology. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merrill Prentice Hall.
I am a professor of Educational Technology. I have worked at several elite universities. I hold a PhD degree from the University of Illinois and a master's degree from Purdue University.